
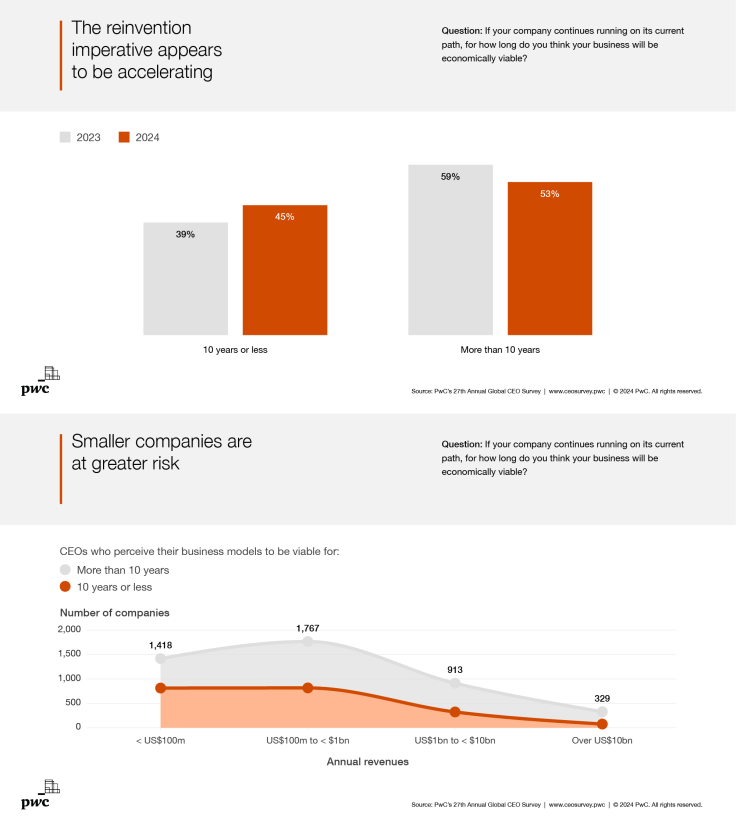
The 27th Annual Global CEO Survey conducted by PwC revealed that 45% of the 4,702 CEOs surveyed express skepticism about their companies' viability in the next decade if they maintain their current trajectory—a notable increase from the 39% reported just a year ago.
The study sheds light on the persistent concerns surrounding long-term sustainability, even as 97% of CEOs have taken steps to adapt to accelerating global megatrends such as technological disruption and climate change.
The urgency to reinvent is intensifying, with CEOs anticipating greater pressure over the next three years from various trends affecting global business. Efficiency remains a major concern, as respondents identify significant inefficiencies in routine activities, estimating that around 40% of time spent on these tasks is inefficient—a potential self-imposed US$10 trillion tax on productivity.
Smaller company CEOs expressed more concerns about viability than their counterparts from larger ones. However, most said they are willing make complex trade-offs for sustainability, with 40% accepting lower hurdle rates for climate-friendly investments.
In the realm of climate change, CEOs report mixed success in meeting objectives. While two-thirds are working on improving energy efficiency, fewer than half have incorporated climate risk into financial planning, and one-third have no plans to do so. Notably, 55% of global GDP, equivalent to about US$58 trillion, is moderately or highly dependent on nature.
Generative AI has also emerged as a critical theme, with CEOs acknowledging its potential for transformative change in the next three years. Those who have adopted generative AI are more optimistic about its impact. However, concerns over cybersecurity risks and the potential spread of misinformation are widespread, emphasizing the societal obligation for responsible AI use.
The report underscores the need for CEOs to continuously reinvent and embrace a broader range of initiatives beyond business models. Recognizing barriers to change, such as infrastructure challenges and workforce skills, they are urged to engage, empower, and enable their teams. As climate change becomes a priority, collaboration with CFOs for sustainable business models is encouraged.
In addition to these insights, the study reveals that geographical variations exist in CEOs' concerns. For instance, inflation remains a top concern for those in the United States, even though this is receding in the rest of the world. Geopolitical threats continue to be a worry for CEOs in Central and Eastern Europe and the Middle East, indicating regional disparities in perceived risks.
Furthermore, CEOs are adjusting their risk thresholds for climate-friendly investments, with 41% indicating lower hurdle rates. This shift in expectations aligns with the sentiment among investors, as two-thirds of them believe companies should prioritize expenditures addressing environmental, social, and governance (ESG) issues, even at the expense of short-term profitability.
The study delves into the potential impact of generative AI on the workforce, revealing that 25% of CEOs expect a reduction in employee headcount by at least 5% in 2024 due to generative AI. However, this reduction may be offset by hiring in other areas, with 39% of CEOs expecting their companies' headcount to increase by 5% or more in the coming 12 months.
The report concludes by emphasizing the critical need for CEOs to challenge conventional wisdom and stay ahead of fundamental changes in their businesses. Effective leadership, alignment between leaders and employees, and a culture of trust are highlighted as essential elements for navigating the evolving landscape. The data suggests a growing premium on leadership effectiveness as companies enter an era of continuous reinvention, presenting CEOs with unprecedented opportunities to reshape their organizations and thrive amidst disruption.
© 2025 Latin Times. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce without permission.





