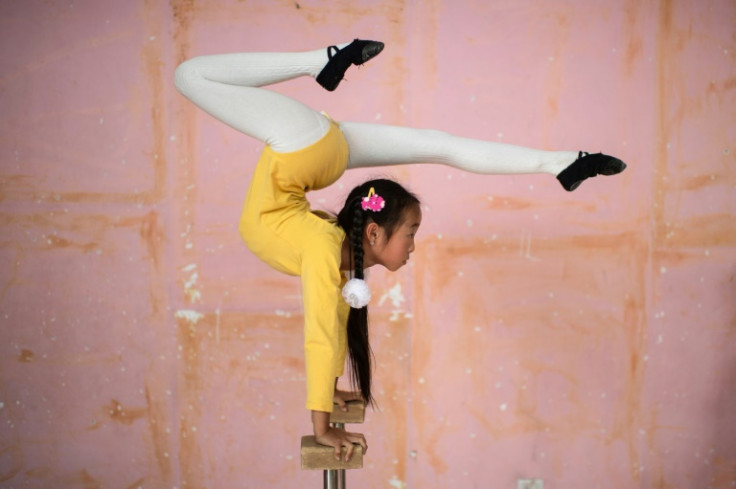
Mongolian circus performers fly through a cavernous hall inspectors have warned could collapse any time, one of the few places left to train if they hope to travel the world with their country's spectacular big top shows.
The decaying, more than a hundred-year-old venue at the Mongolian Circus School is where hundreds of young artists, many now performing at celebrated outfits like Cirque Du Soleil, started their careers.
Defying gravity in a building shaped like a traditional Mongolian ger, the performers practise acrobatics and trapeze, suspended on ropes lashed to the building's dilapidated rafters.
One performer, 18-year-old Uuganbayar Nerguibaatar, said he hopes to follow in his sister's footsteps and take part in international competitions.
"I want to try and become a circus artist," he said.
With paint peeling off the walls and rusty equipment, the building where the artists practice is simply not safe, authorities have warned.
But for the performers, the high-vaulted ceilings provide an ideal space to perfect the daredevil feats that made the Mongolian circus world famous.
"The circus was so popular. We all want to revive it," Gerelbaatar Yunden, a former circus art director, told AFP.
"It is our duty."
The circus was long one of Mongolia's most popular forms of entertainment, bringing crowds from across the country to see breathtaking shows packed with extreme gymnastics, aerial stunts -- and even wild animals.
Its contortionists -- known as Uran Nugaralt, a practice dating back centuries -- were particularly renowned.
But faced with meagre prospects at home, hundreds of the country's top talents have gone overseas in recent years.
"When we go to international competitions and festivals, we're always asked to train international students," Bolortuya Purevdorj, Dean of the Circus Faculty of the Mongolian Conservatory, told AFP.
"But we politely say we don't have enough teachers or human resources," she said.
"We don't have training facilities."
Performers told AFP they estimated about 85 percent of their colleagues live and work abroad, with at least 400 artists in Turkey as well as 500 contortionists in the United States and Europe.
"Antarctica is perhaps the only place that Mongolian circus performers have not performed," Gerelbaatar told AFP.
Mongolia's only modern circus venue was built in the Cold War by Romania as a gift to the socialist ally.
The government sold it in 2007 to Dagvadorj Dolgorsuren, Mongolia's first Sumo champion, who was keen to splash his wealth on investments back home.
He renamed it Asa Circus and it was intended to provide a rent-free training facility for circus students.
But it has instead been used for high-profile concerts and events, with fewer and fewer circus acts taking to the stage in years.
That venue was home to the Mongolian Circus School's only training facilities, leaving few options for performers to hone their craft.
The public school -- which has dozens of students and 15 teachers -- now severely lacks training spaces, with a new venue having been under construction for years.
Performers are demanding the government speed things up.
"Once we build a proper circus school facility, (circus art) will succeed," Gerelbaatar, the former circus art director, told AFP.
After that, he said, "the government can expect results and success" and the Mongolian circus can "rise again".
In the meantime, the school has rented a space far away from its headquarters, forcing students to endure long commutes to train.
"There are a lot of problems. Circus is the art of space, but space is very limited here," Bayarchimeg Erdenebayar, a juggling student, said.
"I will keep improving my skills for another year."
In light of the privatisation, many contortionists split away from the main Mongolian circus to set up smaller, more specialised schools.
During a visit to one such school, AFP saw students twisting themselves into all sorts of weird and wonderful shapes and sizes, legs held high as heads poked through hips.
But teacher Erdenetsetseg Badarch, who trained as a contortionist under the country's Soviet-backed regime and performed thousands of times on the stage of the Mongolian Circus, said the facilities available are far from enough.
"In order to become a circus artist, we need to learn many other aspects of the art such as costume design, stage speech and body language," she said.
"My little studio cannot teach everything."
Another contortionist teacher there said that despite the obvious talent on display, his hopes for the future were bleak unless the state steps in to help.
"Our own state ignores its talented artists, who deserve better recognition," Bud Tumurbaatar told AFP.
"That's why Mongolian artists are leaving Mongolia for other countries for better treatment and a better income."
© 2025 Latin Times. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce without permission.




